Do you know that the boilers used in your pharmaceutical, chemical, steel, refinery, sugar or food industry needs a boiler water testing from an authorised laboratory? There have been several cases of boiler explosion due to catastrophic failure of boilers. The stress corrosion of critical parts of the boiler whether its safety valve or edges of lap joints could be dangerous for the safety and economic operations.
Boiler water testing is an integral part of the routine boiler tests in many industries like Textile, Rubber, Pulp and Paper, Food, Distilleries, Dyers and Paint. A regular boiler water test assures higher efficiency and reduced maintenance of boilers. It is quite essential to maintain correct water conditions by careful monitoring of boiler water to avoid scale formation, reduction in efficiency, steam purity, and corrosive water conditions.
What causes corrosion in boilers?
Dissolved gases
Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and ammonia creates corrosion in boilers as the degree of oxygen depends on concentration of dissolved oxygen, pH and temperature of water.
Dissolved or suspended solids
It increases electrical conductivity of water, higher dissolved solids indicate greater conductivity and eventually causes corrosion
Acidity
High velocity increases corrosion by transporting oxygen to the metal and carrying away the products of corrosion at a faster rate. When water velocity is low deposition of suspended solids can establish localised corrosion cells.
Temperature
Concentration of oxygen along with increased temperature accelerates the reaction so that even a small quantity of dissolved oxygen causes severe corrosion.
A glance at the purpose of boiler water testing.
- To prevent scale formation in the boiler.
- Prevent corrosion in the boiler feed system by maintaining the boiler water’s alkaline condition.
- To remove dissolved gases such as oxygen from water.
- Control sludge formation, thus preventing carry over into the system.
- To determine the impurities and thereby determining the amount of treatment required.
- Maintain and provide residual reserve of chemicals.
- Improve efficiency thereby increasing boiler’s life.
- Exercise careful control over boiler treatment chemicals.
Preventive Measures
- It is important to ensure that the water leaving the deaerator is free of oxygen, as oxygen creates corrosion. The deaerator is operated at the proper pressure, and water is at saturation temperature for the pressure.
- It is essential to make sure that the water is tested periodically. Loss of resin from a softener or demineralizer can create problems if the resin escapes into the feedwater.
- Never use untreated water in a boiler.
- The water side of the boiler should be inspected on a regular basis.
- The water side of the deaerator should also be inspected on a regular basis to ensure that it should be free of corrosion.
Boiler water tests
All the boiler water test kits come with a standardized step-by-step test procedure for various boiler water tests. The main boiler water tests that are routinely carried out are as follows:
- Deha/Oxygen test – For testing oxygen and Chemical content
- Hydrate Alkalinity – For testing the presence of hydrates
- Neutralized Conductivity – For testing the presence of ferrous ions and metal contents.
- Condensate PH – Measuring the acidity or alkalinity of the water.
- Phosphate – For testing the presence of phosphate compounds. It is important to maintain a minimum of 10 ppm of phosphate.
- Feed Water Hardness – For testing the presence of carbonate compounds.
All the test samples should be cooled to 25 degree Celsius with the help of a sample cooler. This is done in order to prevent flashing which concentrates the sample. If the sample is coloured or turbid, filter paper should be used before testing.
Boiler water testing procedure
pH
The pH value of the boiler water is a number between zero and fourteen. Values below seven are acidic, seven is neutral, and values above seven are alkaline. The pH factor influences scale formation and the corrosive tendencies of boiler water. The pH should be maintained between a minimum of 10.5 and a maximum of 11.0 to prevent acidic corrosion of boiler tubes and plates, and to provide for the precipitation of scale forming salts before scale is deposited.
Below a pH of 5.0 the water is acidic enough to dissolve the steel boiler plates. At a pH between 5 and 9.4 pitting of shell plates will occur at a rate depending on the amount of dissolved oxygen in the boiler.
Dissolved Oxygen
Dissolved oxygen is caused by the solubility of atmospheric oxygen in the supply water. Aeration of the city water supply is frequently used to remove other noxious gasses. Efficient aeration results in saturation of the water with oxygen.
The majority of corrosion problems are directly related to the quantity of dissolved oxygen in the boiler water. Elimination of the corrosive effect of dissolved oxygen can be accomplished both directly and chemically.
Direct or mechanical removal of dissolved oxygen is accomplished through the use of a deaerator or by heating the water to a temperature above 180 degrees F. Heating the water can be done with a preheater or sparge tube installed in the return system.
Chemical deaeration is done through the introduction of specific chemicals in the boiler to react with the oxygen. The dissolved oxygen content should be maintained at a minimum but at no time should it exceed 0.007 mg/l.
Sulphites
Sodium sulphite is generally used for the chemical removal of dissolved oxygen within the boiler water. To assure the rapid and complete removal of the oxygen entering the boiler feedwater system the concentration of sulphite in the boiler must be maintained at a minimum of 20 PPM (parts per million).
Solids
Solids can be broken up into two categories: suspended solids and dissolved solids. Suspended solids are those which can be removed by filtration while dissolved solids are in solution with the water. The best test for the determination of solids content of the boiler water is through a conductance test.
The conductance value of boiler water varies by the various ionized salts present. The conductance can be used to measure the total dissolved solids in the boiler water and to serve as an accurate means of the control of solids through the use of blowdown.
Alkalinity
The alkalinity of boiler water should be sufficiently high enough to protect shell and plates against acidic corrosion, but not high enough to produce carryover. A minimum value for alkalinity for adequate protection is 200 PPM.
High boiler alkalinity, which is in excess of 700 PPM, should be avoided. Values higher than this can lead to embrittlement of the steel.
Phosphates
Phosphates are used to react with calcium hardness in the boiler water. It is desirable to keep the concentration of phosphates in the water to 30 – 50 PPM in order for complete reaction of the phosphates with the calcium hardness entering the boiler through the feedwater.
Hardness
In boilers the hardness of the water can cause the formation of scale and sludge. The hardness must be removed in the makeup water to the return system. Total hardness should not exceed 50 PPM.
Oils
Oil causes foaming, or combines with suspended solids to form a sludge which can cause the overheating of boiler plates. If oil gets into the boiler, the boiler should be taken out of service immediately and thoroughly cleaned.
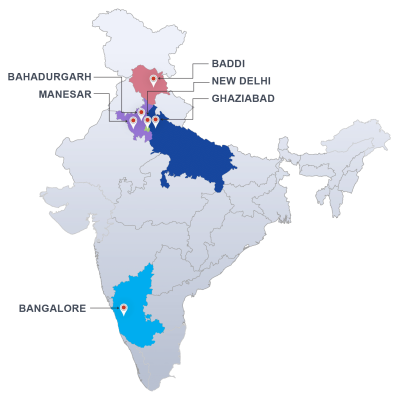
Boiler water test in laboratory
It is essential to get a boiler water test from a certified laboratory for accurate results. Our laboratory has been accredited by NABL to the ISO IEC 17025, since 2003. Water for Boilers as per IS:10496 is tested in our labs. With PAN India footprints, we have testing laboratories in New Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, and Bangalore. Our labs are also approved by the Bureau of Indian Standards for testing of water to various national and international standards. We can help you comply with water regulatory laws and guidelines. Our laboratory has been accredited and notified by NABL, FSSAI, BIS, CDSCO, ISM&H, APEDA, EIC/EIA, AGMARK.
Contact us to get boiler water testing services.