Grow with Us!
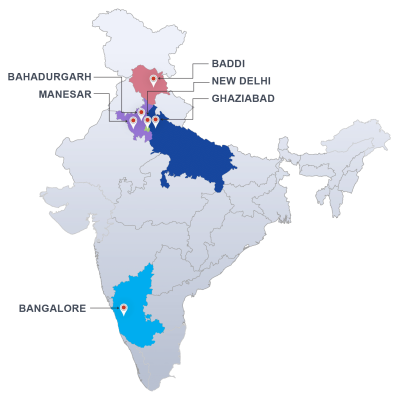
Our food testing laboratories in pan India locations test for processed food, beverages, food additives, agricultural products, food packaging, marine and meat products, fruits and vegetables. We ensure that the food product is free from any physical, chemical and biological hazards or contaminants, such as metals, additives, pesticides, preservatives, cleaning agents, salmonella, e-coli bacteria, etc.
.
Our innovative and client-focused approach makes us your partner with understanding of national and international standards and regulations right from source through production and delivery.